VIsoQLR: an interactive tool for the detection, quantification and fine-tuning of isoforms using long-read sequencing
VIsoQLR is an interactive analyzer, viewer and editor for the semi-automated identification and quantification of known and novel isoforms using long-read sequencing data. VIsoQLR is tailored to thoroughly analyze mRNA expression and maturation in low-throughput splicing assays. This tool takes sequences aligned to a reference, defines consensus splice sites, and quantifies isoforms. Users can edit splice sites through dynamic and interactive graphics and tables as part of their manual curation. Known transcripts, or isoforms detected by other methods, can also be imported as references for comparison.
A command line version is available at https://github.com/TBLabFJD/Mini-IsoQLR
Cite this article
To know more about VIsoQLR have a look at the article in Human Genetics: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00439-023-02539-z
Núñez-Moreno G, Tamayo A, Ruiz-Sánchez C, Cortón M, Mínguez P. VIsoQLR: an interactive tool for the detection, quantification and fine-tuning of isoforms in selected genes using long-read sequencing. Hum Genet. 2023 Mar 7. doi: 10.1007/s00439-023-02539-z. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36881176.
Check our video tutorial
Developers
Main developers
- Gonzalo Núñez Moreno
Contact
- Gonzalo Núñez Moreno (gonzalo.nunezm@quironsalud.es)
License
Mini-IsoQLR source code is provided under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0). Mini-IsoQLR includes several third party packages provided under other open source licenses, please check them for additional details.
Installation
VIsoQLR has been wrapped into a Docker image. To set it up:
- Install Docker following the instructions in https://www.docker.com/. Docker is available for Linux, Windows and Mac users. For windows users, as the image has been developed for Linux kernel, it is necessary to install Linux on Windows with WSL2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux) following the instructions in https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install.
- Once installed type on your shell (or Windows PowerShell in Windows once Docker Desktop has been initialized):
This will download the latest version of VIsoQLR image. This image has already all programs, packages and requirements needed to run VIsoQLRdocker pull tblabfjd/visoqlr:latest
Run VIsoQLR
To run VIsoQLR type on your shell (or Windows PowerShell in Windows once Docker Desktop has been initialized):
docker run -it -p 8888:8888 tblabfjd/visoqlr:latest
This will display some text on the shell and once the line Listening on http://0.0.0.0:8888 appears go to the browser and type http://0.0.0.0:8888 on Linux systems or http://localhost:8888 on Windows systems. If successful you will see:
Click on 'Browse...' button to navigate to your file system to upload your aligner reads in GFF3, BED6, or BAM file format. Once selected the program will automatically run with its default parameters to identify and quantify isoforms. and you will see something like this:
Features
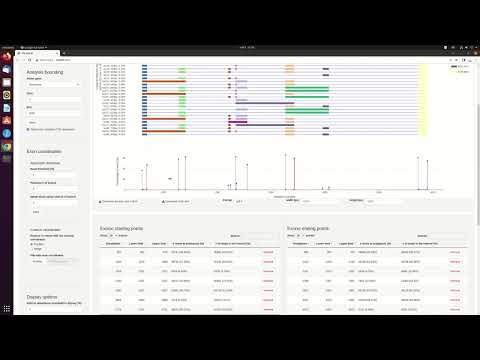
Analysis bounding: this panel allows the user to change the analyzed gene and/or the region of study. Mapped regions outside the selected region will be ignored. This can be used to focus the analysis in a section of the gene.Exon coordinates: Automatic detection: This panel contains three parameters used for the automatic detection of consensus exon coordinates (CECs). TheRead threshold (%)is used to select candidate CECs above this value based on the proportion exon coordinates among all reads. ThePadding (# of bases)are the number of bases at each side of a candidate CES where other non-candidate CEC (below range in the frequency filter) are merged. TheMerge close splice sites (# of bases)is used to merger candidate CESs into the most frequent one if they are closer than the given distanceExon coordinates: Custom coordinates: This panel allow the user to uploaded known or previously defined splice sites to replace or merge with the existing ones. This accepts as an input the exon coordinate file that can be downloaded from the Exonic starting/ending points panel.Display options: allows you to modify the aspect and number of elements of the plotDefined isoforms for comparison: This panel allows you to uploaded transcripts for visual comparison.- Figure panel: the figure is rendered using Plotly which allows the user to zoom in and move through the figure. The color code is used to identify identical exons. Below isoforms, the frequency of start (blue) and end (red) coordinates are shown. The consensus exon coordinates (CECs) are marked with a dot on each bar, and the exact coordinate and frequency are displayed with the cursor over. It is possible to download a screenshot of what is displayed at the moment by clicking the camera icon in the top-right corner. It is also possible to download the whole figure in a dynamic plot (in HTML) and static plot in multiple formats.
- Exonic starting/ending points panel: Editable table where the user can add, delete and modify CECs.
- Isoform information panel: Table which provides extra isoform information.
- Exon information panel: Table which provides extra exon information.
Run sequence alignment using VIsoQLR
One initiated click on "Mapping" in the top-left. You should see something like:
 The screen is divided in 3 panels. The first one is used to build the reference index used by GMAP by uploading the reference sequence(s). Once you upload your sequence(s) the index building will start automatically. Once is complete, a download bottom will appear on the screen. The second panel is dedicated to align the raw reads (in FASTQ format) using GMAP. To do so, upload the ZIP file downloaded from the previous panel as the reference index, the FASTQ file, chose the number of threads and click
The screen is divided in 3 panels. The first one is used to build the reference index used by GMAP by uploading the reference sequence(s). Once you upload your sequence(s) the index building will start automatically. Once is complete, a download bottom will appear on the screen. The second panel is dedicated to align the raw reads (in FASTQ format) using GMAP. To do so, upload the ZIP file downloaded from the previous panel as the reference index, the FASTQ file, chose the number of threads and click Run mapping. Once the reads alignment is done, a download bottom will appear to retrieve the mapped sequences. In case of selecting the BAM option as an output, two download bottoms will appear: the mapped reads (BAM) and its index (BAI). The BAI file is require, for example, to upload the BAM file in IGV. The last column performs the alignment using Minimap2. In this case the reference must be in FASTA format (the same file used to build the GMAP index in the first panel). Although two major solutions for the alignment are made available, we recommend using GMAP as Minimap2 has problem aligning small exons. This limitation is advised in their GitHub (https://github.com/lh3/minimap2), in the “Limitations” section.
Version History
main @ 9c6bc41 (earliest) Created 12th Aug 2025 at 13:48 by Yolanda Benítez Quesada
article link
Frozen
 main
main9c6bc41
 Creators and Submitter
Creators and SubmitterCreators
Not specifiedSubmitter
Views: 550 Downloads: 132
Created: 12th Aug 2025 at 13:48
 Attributions
AttributionsNone
 View on GitHub
View on GitHub